Heat loss using furnace runtimes and outdoor temperatures?
I am trying to calculate my homes heat loss as I am looking into adding more mini splits to carry more of my heating/cooling load. I have been impressed with the one I installed in my downstairs so far. I have solar panels and would like to add another mini split or two and use less of my oil furnace. I want to try and get the sizing right as I think my 80k oil btu furnace is way oversized.
I have had a Effergy whole house electricity monitor installed for a couple years that logs all my electrical usage. My furnace running shows up on the charts for exactly how long it ran for. I also have a weather station that has logged all my outside temperatures as well. Trying to decipher the data to see if I can calculate my heat loss using it. Looking on at the data on a 10 degree night, my 80kbtu furnace was running for 15-20 mins, was off for 30 mins then back on. A 20 min cycle would be about 16k btu so with about 2 per hour would a 30k btu loss seem correct?
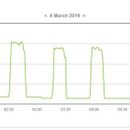
I attached a run time graph of the furnace on a 10 degree night.
GBA Detail Library
A collection of one thousand construction details organized by climate and house part








Replies
For a quick calculation.....Q = -k A (T2 - T1) or k = - Q / A * (T2 -T1)
Where Q is the amount of BTU used in an hour , k is conductivity or heat loss in BTU/ hr *ft^2 * F , A would be the exterior surface area ft^2 and (T2 -T1) is the temperature difference F, just to give you a basic overall heat loss or rate.
Timing furnace run time is a way to calculate building heat loss. I have done it for my own home on a cloudy winter day with a steady state temperature, over the course of 8 hours. The furnace efficiency is part of the calculation, hopefully this is known. It is then a matter of Btu's used per hour divided by the Delta T for an hourly Btu heat loss per degree F.
@BFW577, it's a bit hard to read the times off of that graph. Can you pull the exact times from the Effergy dashboard? It would also be helpful to know the manufacturer and model number of your furnace. (Both should be stamped somewhere on your furnace.)
The formula you want is
space load = (furnace capacity) * (percent ON time)
By "furnace capacity", I mean the furnace's thermal power output, in kBTU/h. Note that this is smaller than the furnace's fuel use (thermal power input) by a factor of the furnace's efficiency.
Eyeballing your graph, I see about 80 minutes of ON time between 2:30 and 6 AM (210 minutes total), so
percent ON time = (80 minutes) / (210 minutes) = 38%
Clarify that number from your software if you can. Assuming it's roughly accurate, and that your furnace capacity is 80 kBTU/h (clarify this from the manufacturer specs if possible), we get
space load = (80 kBTU/h) * (38%) = 30 kBTU/h
You should also verify that you have a single-stage (OFF/ON) furnace, rather than a two-stage (OFF/LOW/HIGH) furnace. That's usually easy to figure out from the manufacturer spec sheet.
By the way, 10 F may not be the recommended design temperature for your location. Check here:https://articles.extension.org/sites/default/files/7.%20Outdoor_Design_Conditions_508.pdf
To estimate your design load, you just need your design temperature (the "Heating 99% Dry Bulb" number from the link above) and your indoor air temperature setpoint:
design load = (load at 10 F) * (setpoint - design temperature) / (setpoint - 10 F)
For example, if your setpoint is 68 F and your design temperature is 1 F, then
design load = (30 kBTU/h) * (68 F - 1 F) / (68 F - 10 F) = 35 kBTU/h
The duct losses are only relevant if the ducts are outside the conditioned envelope of the house.
Yeah, that's a good point. I edited the duct losses out. It's true that they aren't always relevant. Even when they are, duct efficiency is a tough number to pin down. Also, leaving duct losses out leads to conservative (over-)estimates, so it should be fairly harmless.
This is another way to do it pretty accurately based on consumption.
//m.etiketa4.com/article/out-with-the-old-in-with-the-new
With run times make sure you compensate for the delay before the flame is established, if you have short run cycles the pre purge time good be significant enough to skew your numbers.
Yeah, the fuel use method in that article is another good option.
For a third approach, have a go at a Manual J load calculation using this free online app:
http://www.loadcalc.net
Manual J estimates are prone to "garbage in, garbage out" errors - it's hard to know all the required R-values, air change rates, etc. - but it's another data point. If all three estimates (furnace timing, fuel use, Manual J) land in the same ballpark, you can be pretty confident you have a handle on your design load.