How do you include an eco-roof into a home energy audit?
What criteria is used to make the rating? Most eco-roofs support many types of living materials. They are also built to stronger specs, and with that bring new challenges of being more air tight. How does that affect the building envelope?
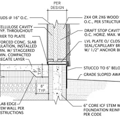
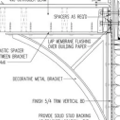
GBA Detail Library
A collection of one thousand construction details organized by climate and house part








Replies
Rory,
Vegetated roofs will have only a minor effect on the thermal performance characteristics of a building's envelope. As reported inEnvironmental Building News(November 2001), "Note, however, that while green roofs offer significant energy-saving potential, there are less expensive ways to accomplish similar savings — such as installing reflective Energy Star roofs or increasing insulation levels. And while green roofs are great for reducing cooling loads, they are not as effective at reducing heat loss during cold weather — soil and specialized planting media do not insulate very well. In most situations, a layer of insulation should be added to the roof assembly."
The R-value of soil is typically quite low — as low as R-1 per foot, although lighter soil media used for roofs will have a higher R-value. Consult your soil supplier to get specific information on the medium's R-value.
As far as airtightness is concerned, a vegetated roof should behave exactly the same as any other roof with membrane roofing, which is a common type of commercial roofing. In general, there is very little air leakage through membrane roofing.
If thermal performance is your main concern, your best bet is to skip a vegetated roof and beef up the roof's insulation thickness. However, if you have decided to install a vegetated roof for other reasons, be prepared to spend more for the same thermal performance you would get with traditional materials.