在氢气加热的平板下进行绝缘
I am building a garage in CA zone 16, US zone 4B. Last year I buried temperature recorders at depths of 18″ and 42″. The deeper probe hovered at 33 degrees all winter. The shallower probe occasionally froze to 31 degrees. Well water from 200 ft deep is typically 40 degrees.
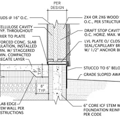
该建筑物将具有8英寸的结构板,以支撑一些集中的负载。对我来说,能够在平板中的任何地方钻锚孔很重要,因此我想将水力管放在平板的底部。
My current plans call for 8″ aggregate base and 2″ EPS under the slab, with the tubing on top of rebar at the mid height of the slab. If I move the hydronic tubing to the bottom of slab should I be adding more insulation under the slab? Also, in theory, air entrained concrete has a high R value that would limit efficiency of a hydronic system but I have seen opinions ranging from “air entrained R value is same as normal concrete” to “air entrained R value is 10x normal concrete”. I will pour the slab after the building is in place so conceivably I could order non-air entrained concrete.
顺便说一句,平板外围绝缘是R10,很难增加这么多。我能做的大多数是在霜墙内部添加另一个R5。
If it is relevant, my heating objective for the structure is 60 degrees F minimum air temp, with no variation 24×7. I want to keep plumbing and stored equipment from freezing and want to be able to work without my fingers freezing. I will be on time of use electric billing so am hoping to use a time of day thermostat to electrically heat the slab at night and then use its substantial thermal capacity to keep temperature reasonable during the day.
GBA Detail Library
A collection of one thousand construction details organized by climate and house part








答复
EPS的2英寸不多。我认为Martins在其中一篇GBA文章中的建议是,地板热量有多少隔热材料?更多的。
I did 3” in my basement, and 2” for the picture frame. This is in Zone 4A Marine. The tubes were supported on a wire mesh sitting on chairs.
In terms of tube depth, you want the tubes to end up about 1.5” or so from the top of the concrete. John Seigenthalers book has a whole chapter on this. The further down you go, you need to be to add more heat (hotter input water) to get the same warming effect.
>"The building will have an 8″ structural slab to support some concentrated loads. "
Air entrained or not, the thermal mass/R value thermal diffusivity and lag time of an 8" slab makes it nearly impossible to use as a heating radiator without major undershoots & overshoots.
>“我目前的计划要求8英寸的总底部和2英寸的EP,在平板中部高度的钢筋顶部的管道上。”
That makes it even MORE impossible to control, since it increases the lag time to the max!
If radiant floor is a "must", an above-the slab solution with at least some amount of thermal isolation from the slab would be needed. A minimalist Roth panel above the slab would be one solution to making it more responsive, but wouldn't allow you to game the TOU rate structures without using buffer tanks.
R8.4 isn't much insulation to put between an 80F+ slab and near-freezing dirt with 40F subsoil. It should probably be something like twice that.
为了有机会使用板,因为散热器和存储介质需要进行一些数学,因此可以很好地做到这一点。(而且这不是“ Web Forum设计”餐巾纸的问题。)
假设有1500平方英尺(使数学简化)具有8英寸厚度,您的混凝土中有1000英尺^3。它的容量约为32kbtu/degf,这并不是那么多。要说它在12h时期工作,您将需要大约10kbtu的房屋热量损失。
Asssuming 75F slab, 40F ground with 2" you would loose around 6200BTU to the ground. That is a fair bit compared to the house load above. You would probably want around 5" to 6".
Overall, it is possible to make it work, but you need to do some real thermal simulations, much more than the quick calcs above. Probably no way to make it work without a highly insulated envelope.
As Dana said, controlling this would not be easy, if your place has a lot of solar gain, it would cause a lot of overheating when the sun is out.
混凝土是一个非常好的热导体,具有任何合理量的绝缘波纹管(超过2英寸),管道的位置对能量损失几乎没有差异。放置管道降低降低条纹,因此您可以使用较大的条件跑步之间的间距。